NGAL Biomarker
The NGAL biomarker provides early assessment of acute kidney injury.
An Early Warning Signal
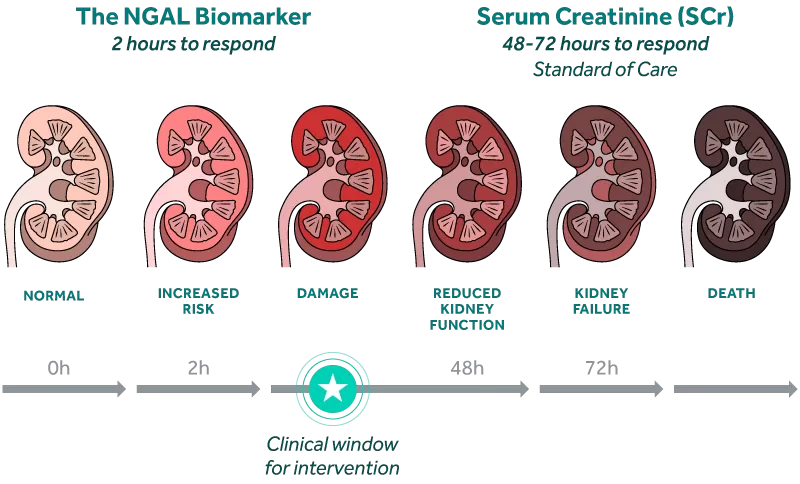
The NGAL biomarker rises rapidly in response to kidney injury, preceding changes in creatinine by as much as 2 to 3 days.i
The NGAL biomarker has been shown to offer early clinical decision support to guide patient managementii,iii. By identifying patients at risk of AKI early, clinicians can take more appropriate action to manage fluid levels, avoid nephrotoxic agents, and potentially prevent permanent kidney damage.i
“Damage biomarkers like NGAL are an early warning signal to trigger interventions such as the KDIGO bundle.”
– DR. PRASAD DEVARAJAN, co-discoverer NGAL BIOMARKER
An Ideal Damage Biomarker
FAST
NGAL responds just 2 hours after kidney injuryiv and 2-3 days before serum creatinine rises.i
ADDITIVE
NGAL+ identifies subclinical AKI when serum creatinine alone failed to identify 43% of AKI.v
PROGNOSTIC
Identifies patients at risk of developing moderate to severe AKI.vi
RESULTS
Improved management of AKI can reduce LOS, minimize unnecessary interventions, and inform treatment choices.vii
CLINICALLY RELEVANT
The NGAL biomarker has been studied in over 16,500 patients in numerous settings including post-cardiac surgery, in critical illness, and post kidney transplantation. In each setting, “NGAL significantly improved the prediction of AKI risk over the clinical model alone.” viii
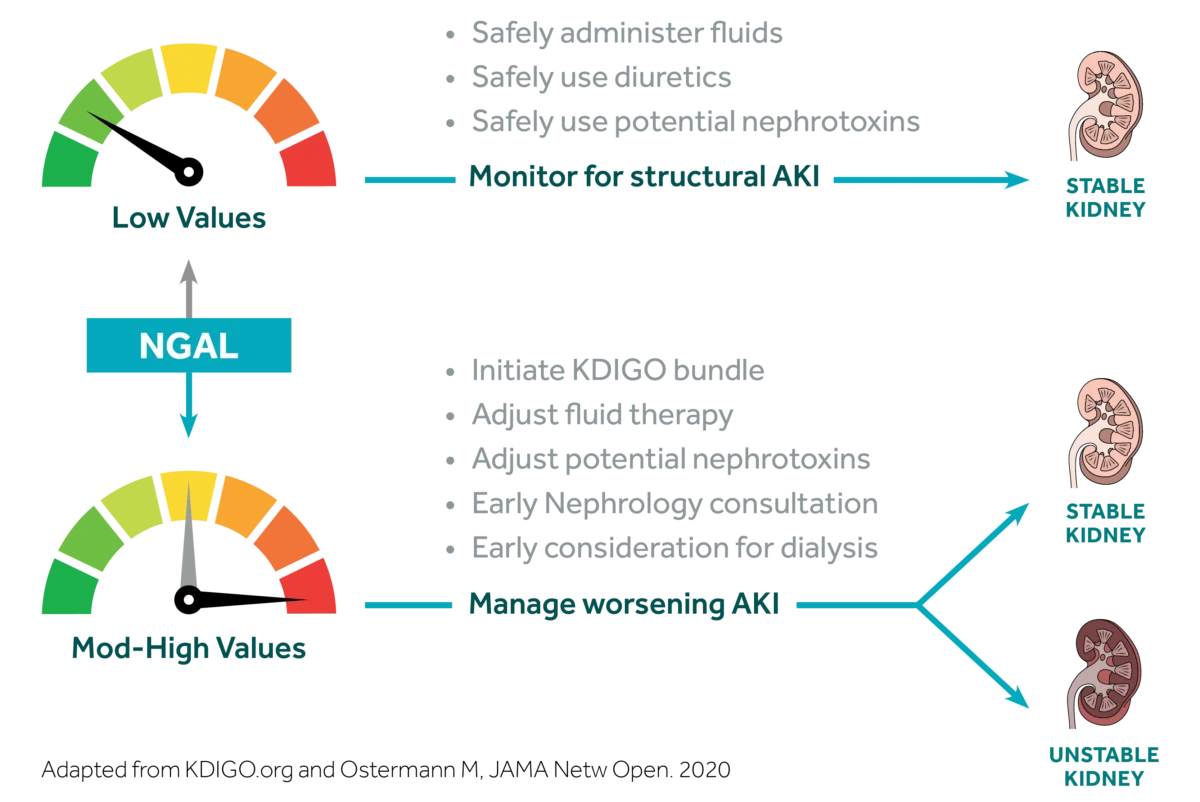
Value of an NGAL Result
Used in conjunction with clinical evaluation, NGAL provides additional data to clarify a patient’s AKI risk.
Similar to troponin for myocardial infarction, NGAL offers clinicians insight into AKI. Know days earlier which patients you need to worry about.
NGAL: The #1 Kidney Biomarker in Research
- Over 2,500 publications on PubMed in both human and animal studies.
- A CDER-qualified kidney tubular injury urinary biomarker for use in Phase 1 trials.
- FDA and EMA support the use of NGAL as a safety biomarker for early identification of renal toxicity.
BioPorto’s NGAL ELISA kits are available in six species – the bridge from pre-clinical research to clinical trials.
BioPorto’s NGAL products are marketed under applicable registrations in several countries worldwide. Learn about our clinical and research products outside the US by visiting our global site.

i Devarajan P. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: a promising biomarker for human acute kidney injury. Biomark Med. 2010;4(2):265–280.
iiMurray PT, Mehta RL, Shaw A, et al. Potential use of biomarkers in acute kidney injury report and summary of recommendations from the 10th Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative consensus conference. Kidney Int. 2014.85(3):513-521
iiiStanski N, Menon S, Goldstein SL, Basu RJ. Integration of urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin with serum creatinine delineates acute kidney injury phenotypes in critically ill children. Journal Critical Care. 2019.53:1-7.
ivKrawczeski CD, Goldstein SL, Woo JG, et al. Temporal relationship and predictive value of urinary acute kidney injury biomarkers after pediatric cardiopulmonary bypass. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58(22):2301–2309.
vHaase M, Devarajan P, Haase-Fielitz A, et al. The outcome of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin-positive subclinical acute kidney injury: a multicenter pooled analysis of prospective studies. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57(17):1752–1761.
viZappitelli M, Washburn KK, Arikan AA, et al. Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is an early marker of acute kidney injury in critically ill children: a prospective cohort study. Crit Care. 2007;11(4):R84.
viiVarnell CD Jr, Goldstein SL, Devarajan P, Basu RK. Impact of Near Real-Time Urine Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Assessment on Clinical Practice. Kidney Int Rep. 2017 Jun 3;2(6):1243-1249.
viiiHaase-Fielitz A, Haase M, Devarajan P. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a biomarker of acute kidney injury: a critical evaluation of current status. Ann Clin Biochem. 2014;51(Pt 3):335–351.
