The First FDA-Cleared Test for Pediatric AKI
ProNephro AKI™ (NGAL) for risk assessment – available through Roche Diagnostics.
A Critical Addition to Acute Kidney Care
ProNephro AKI (NGAL) provides an additional data point for clinicians to identify patients ≥3 months to <22 years at risk of developing or having persistent, moderate-to-severe AKI within 48-72 hours after intensive care unit (ICU) admission.
Make complex and potentially life-saving care decisions earlier and more confidently.
Cardiovascular
compromise
Respiratory
compromise
Solid organ
transplant
BONE marrow
transplant
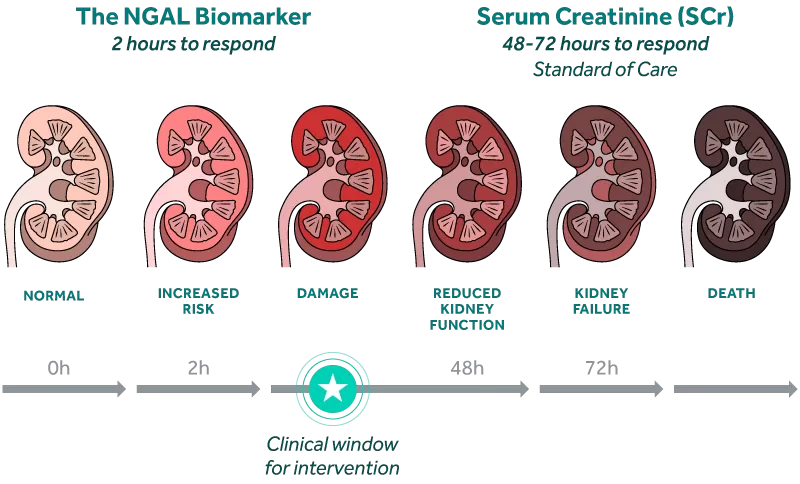
Capitalize on the Window of Clinical Intervention
The NGAL biomarker rises rapidly in response to kidney injury, preceding changes in creatinine by as much as 2 to 3 days.i
By identifying patients at risk of AKI early, clinicians can take more appropriate action to manage fluid levels, avoid nephrotoxic agents, and potentially prevent permanent kidney damage.i
Stay up to date
Join our mailing list for product news and the latest AKI and NGAL research.
Identify AKI Days Earlier than SCr
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) is difficult to assess early because the current standard of care relies on changes in serum creatinine (SCr) and urine output, physiologic endpoints that are delayed, non-specific, and impacted by extrarenal factors such as nutrition status and muscle mass.ii

“I have changed my management decisions on rounds and definitely changed the way I approached different patients based on NGAL results.”
– PCICU Intensivist
About ProNephro AKI (NGAL)
A particle-enhanced turbidimetric immunoassay for the in vitro quantitative determination of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL).
Sample type
3 µL urine
Assay run time
~ 10 minutes on Roche cobas c 501 analyzer
Result availability
Similar to a comprehensive metabolic panel; varies according to your laboratory’s collection and processing schedule
Clinical Studies
Immunoassay for the in vitro quantitative determination of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in human urine.
Determination of NGAL is intended to be used in conjunction with clinical evaluation in pediatric patients (≥ 3 months to < 22 years) without underlying kidney disease admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) for the management of cardiovascular or respiratory compromise or who have had a solid organ or bone marrow transplant.
ProNephro AKI™ (NGAL) is intended to be used in the first 24 hours of ICU admission. In patients with low SCr levels, indicative of no acute kidney injury (AKI) or AKI Stage 1, the test can be used as an aid to identify patients at risk to develop moderate to severe AKI (Stage 2/3) 48 to 72 hours after the assessment. In patients with an elevated SCr level, indicative of Stage 2/3 AKI, the test can be used as an aid to identify patients at risk of having persistent moderate to severe AKI (Stage 2/3) 48 to 72 hours after the assessment.
The particle-enhanced turbidimetric immunoassay is intended for use on the Roche cobas® c 501 clinical chemistry analyzer.
*FDA-cleared for use in the United States.
i Devarajan P. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: a promising biomarker for human acute kidney injury. Biomark Med. 2010;4(2):265–280.
ii Moledina DG, Parikh CR. Phenotyping of Acute Kidney Injury: Beyond Serum Creatinine. Semin Nephrol. 2018;38(1):3–11.
iii Post Hoc AWARE: Kaddourah A, Basu RK, Goldstein SL, Sutherland SM; Assessment of Worldwide Acute Kidney Injury, Renal Angina and, Epidemiology (AWARE) Investigators. Oliguria and acute kidney injury in critically ill children: implications for diagnosis and outcomes. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2019 Apr;20(4):332-339.
